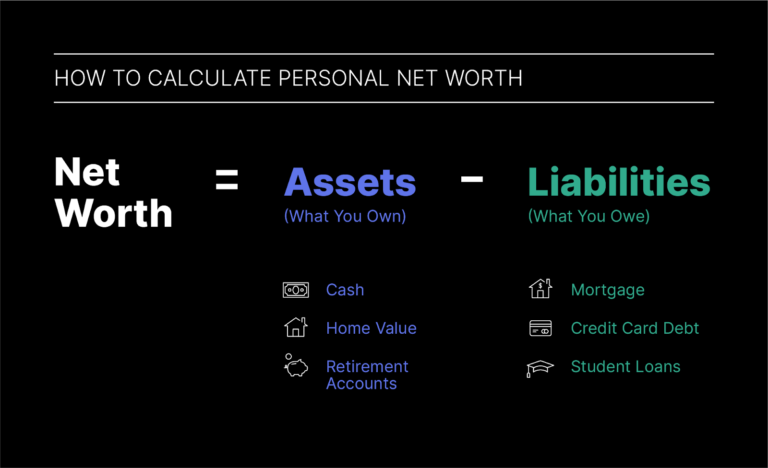
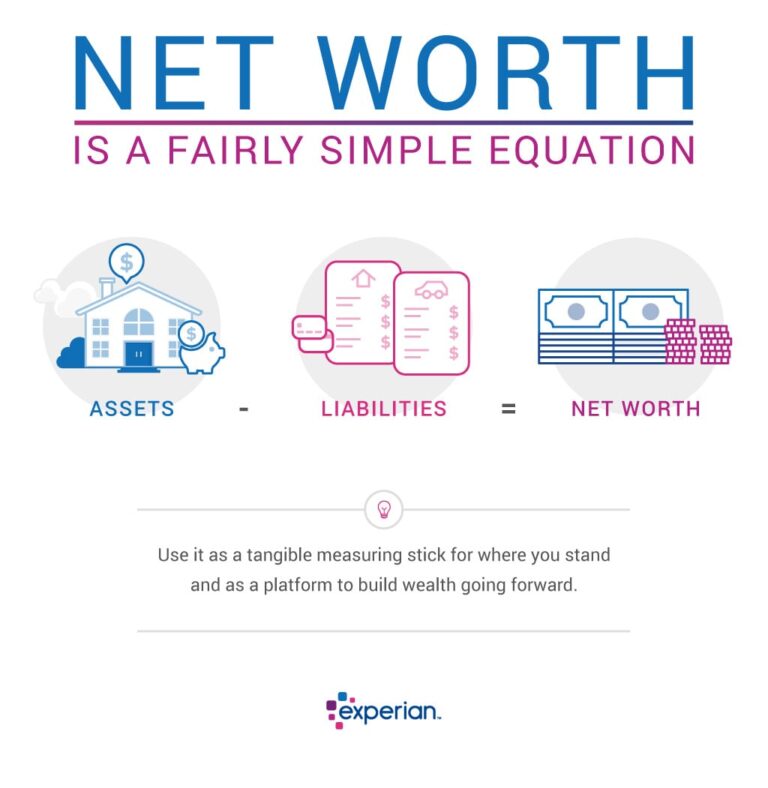
In our rapidly evolving digital landscape, the term technomap” has emerged as a pivotal concept shaping how we understand and interact with technology. Unlike traditional maps that chart physical geography, technomaps offer a dynamic visualization of the digital terrain that defines our modern existence. From mapping out data flows and cybersecurity landscapes to tracking trends in artificial intelligence and virtual reality, technomaps provide invaluable insights into the complex interplay between technology and society.
Unveiling the Layers of Technomaps
Technomaps are multifaceted tools that help us comprehend and navigate various dimensions of the technological realm:
- Data Landscapes: At the core of technomaps lies the visualization of data ecosystems. These maps illustrate how data moves within and between systems, offering a clearer picture of information flows, from collection to analysis and storage.
- Emerging Technologies: Technomaps also chart the trajectory of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and quantum computing. By mapping out the development and adoption patterns of these technologies, researchers and innovators can identify potential applications, predict market trends, and strategize for future advancements.
- Digital Infrastructure: Another critical aspect of technomaps is mapping digital infrastructure. This includes networks, servers, and communication pathways that underpin our digital connectivity.
Technomaps have transformative implications across various sectors:
- Healthcare: In healthcare, technomaps can visualize patient data flows, streamline medical records management, and enhance telemedicine capabilities.
- Finance: In the financial sector, these maps aid in tracking financial transactions, detecting fraud, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Urban Planning: For urban planners,
help optimize transportation networks, manage smart city initiatives, and improve energy efficiency through IoT (Internet of Things) integration.
- Education: In education, technomaps support personalized learning experiences, track student progress, and facilitate the adoption of digital learning tools.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While technomaps offer tremendous potential, they also present challenges and ethical considerations. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the digital divide must be carefully addressed to ensure that technomaps serve the collective good without perpetuating inequalities or infringing upon individual rights.
The Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the evolution of technomaps promises to be transformative. Advances in data visualization techniques, machine learning algorithms, and collaborative platforms will further enhance their accuracy, accessibility, and utility across diverse domains. As we continue to chart new territories in the digital age, technomaps will play an increasingly integral role in shaping our understanding of technology’s impact on society and guiding us towards a more inclusive and sustainable future.
In conclusion, technomaps are not just tools for navigation but windows into the complex interconnections of our digital world. By harnessing their power, we can navigate the challenges and opportunities of the technological landscape, paving the way for innovation, progress, and responsible stewardship of our digital future.